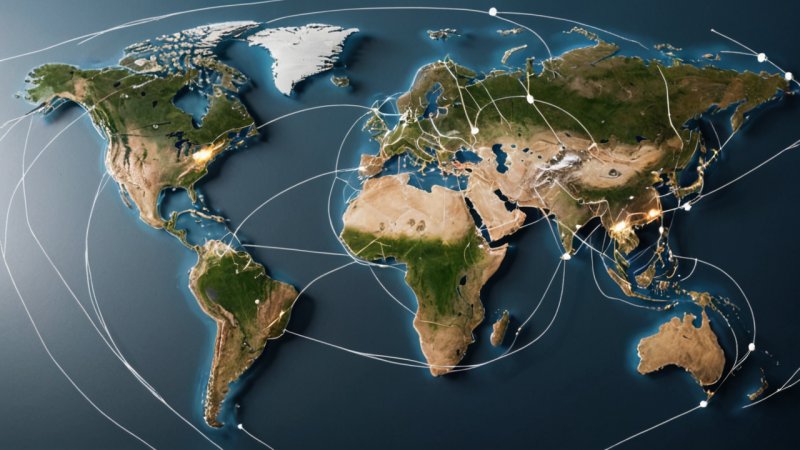
Globalization is a multifaceted phenomenon that has significantly transformed the business landscape across the globe. It encompasses the increased interconnectedness and interdependence of economies, cultures, and populations, primarily driven by trade, investment, and technology. As businesses seek to expand their reach beyond domestic markets, the implications of globalization are profound, affecting everything from corporate strategies to consumer behaviors. This article delves into how globalization is reshaping the business world, examining its drivers, impacts on various industries, challenges, and future trends.
Understanding Globalization
At its core, globalization refers to the process through which businesses and other organizations develop international influence or operate on an international scale. This phenomenon has been catalyzed by advancements in technology, such as the internet and transportation, which have made it easier and more cost-effective for companies to enter foreign markets. The rise of multinational corporations (MNCs) exemplifies this trend, as they leverage global supply chains, labor markets, and customer bases.
Drivers of Globalization
Several key factors drive globalization, including:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in communication and transportation technologies have significantly reduced the barriers to entry for businesses seeking to operate globally.
- Trade Liberalization: The reduction of tariffs and trade barriers through international agreements has facilitated the flow of goods and services across borders.
- Economic Forces: The pursuit of new markets, cost efficiencies, and competitive advantages drives companies to expand internationally.
- Cultural Exchange: Globalization fosters cultural exchange, influencing consumer preferences and business practices worldwide.
Impacts of Globalization on Business
Market Expansion
One of the most significant impacts of globalization is the opportunity for market expansion. Companies can now reach consumers in distant countries, increasing their potential customer base. For example, tech giants like Apple and Google have successfully penetrated international markets, tailoring their products and marketing strategies to local preferences.
Increased Competition
While globalization opens new markets, it also intensifies competition. Local businesses now compete not only with domestic companies but also with international players. This competition can lead to innovation and improved quality, but it can also pose challenges for smaller firms that may struggle to compete.
Supply Chain Optimization
Globalization has led to the creation of complex global supply chains. Companies can source materials and labor from different parts of the world to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. For example, many electronics manufacturers source components from various countries to assemble products at lower costs, ultimately benefiting consumers through lower prices.
Workforce Diversity
With globalization, businesses are increasingly leveraging a diverse workforce. Hiring talent from different cultural backgrounds fosters innovation and creativity, essential for navigating the global market. However, managing a diverse workforce also presents challenges in terms of communication, cultural differences, and integration.
Challenges of Globalization
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Operating in multiple countries exposes businesses to various regulatory environments. Companies must navigate different legal systems, trade regulations, and labor laws, which can be complex and time-consuming. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage.
Economic Vulnerability
Globalization can increase vulnerability to economic fluctuations. A crisis in one part of the world can have ripple effects on global markets, impacting companies' performance regardless of their geographic location. The COVID-19 pandemic is a prime example, revealing how interconnected economies can amplify risks.
Ethical Considerations
As companies expand globally, they must consider ethical practices in their operations. Issues such as labor rights, environmental impact, and corporate social responsibility come to the forefront. Companies that fail to address these concerns may face backlash from consumers and activists.
Future Trends in Globalization
As globalization continues to evolve, several trends are emerging that will shape the future of business:
- Digital Transformation: The digital revolution is accelerating globalization, with e-commerce enabling businesses of all sizes to reach global audiences.
- Focus on Sustainability: Companies are increasingly prioritizing sustainable practices in response to consumer demand and regulatory pressures.
- Resilience Planning: Businesses are adopting strategies to enhance resilience against global disruptions, focusing on supply chain diversification and risk management.
- Local Adaptation: While globalization promotes standardization, companies recognize the importance of adapting their products and services to local markets.
Conclusion
Globalization is undeniably a driving force in the modern business world, offering both opportunities and challenges. As companies navigate this complex landscape, they must embrace innovation, adapt to changing market dynamics, and remain mindful of ethical considerations. The future of globalization will be shaped by advancements in technology, shifts in consumer behavior, and the ongoing quest for sustainability. By understanding and strategically responding to these trends, businesses can thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.