As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, the role of technology has never been more pivotal. From satellite imagery to artificial intelligence, advancements in technology are providing unprecedented insights into the planet's changing climate. These innovations not only enhance our understanding of environmental changes but also empower policymakers, scientists, and communities to take informed actions. In this article, we will explore how various technologies are being harnessed to monitor climate change, the importance of data collection, and the implications for future sustainability efforts.
Satellite Technology and Remote Sensing
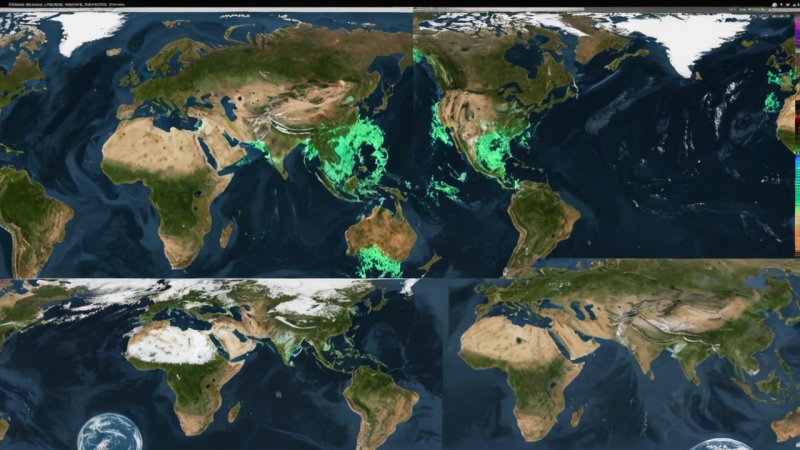
One of the most significant advancements in climate monitoring has been the use of satellite technology. Satellites equipped with remote sensing capabilities allow scientists to collect data on atmospheric conditions, land use changes, and ocean temperatures from space. This technology has revolutionized our ability to track climate change indicators over large geographical areas.
For instance, NASA's Landsat program has been instrumental in providing detailed images of Earth's surface for over four decades. These images help researchers analyze deforestation, urban sprawl, and agricultural practices, all of which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, satellites such as the European Space Agency's Copernicus Sentinel missions provide near-real-time data on air quality and greenhouse gas concentrations, enabling timely responses to environmental crises.
Climate Modeling and Simulation
Another critical area where technology plays a role is in climate modeling and simulation. Advanced computer models simulate the Earth's climate system, allowing scientists to predict future climate scenarios based on various variables such as greenhouse gas emissions, solar radiation, and land use changes.
These models help researchers understand potential impacts on weather patterns, sea level rise, and biodiversity loss. For example, the Community Earth System Model (CESM) is widely used to simulate interactions between the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. By inputting different scenarios, scientists can assess the risks associated with climate change and propose mitigation strategies.
Data Collection and Big Data Analytics
The advent of big data has transformed how climate data is collected and analyzed. With the proliferation of sensors, IoT devices, and mobile applications, vast amounts of environmental data are generated daily. This data can be leveraged to monitor climate change effects at local, regional, and global scales.
For instance, organizations like the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) collect data from various sources, including weather stations, ocean buoys, and atmospheric satellites. By employing big data analytics, researchers can identify trends, correlations, and anomalies in climate data, leading to more accurate assessments of climate change impacts.
Artificial Intelligence in Climate Research
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another transformative technology in the field of climate monitoring. Machine learning algorithms can analyze complex datasets far more efficiently than traditional methods. AI can identify patterns in climate data that may not be immediately apparent to human researchers.
For example, AI has been used to predict extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods, by analyzing historical weather data and current atmospheric conditions. These predictions can help communities prepare and respond more effectively to climate-related disasters. Additionally, AI can optimize energy consumption in smart grids, reducing carbon footprints and enhancing sustainability efforts.
Community Engagement and Citizen Science
Technology is also fostering community engagement in climate monitoring through citizen science initiatives. Mobile applications and online platforms enable individuals to contribute to climate research by collecting data on local weather patterns, wildlife sightings, and environmental changes.
Projects like iNaturalist and Climate Watch encourage people to document their observations, which can then be used by researchers to track biodiversity changes and assess ecosystem health. This grassroots approach not only empowers individuals but also raises awareness about climate issues and fosters a sense of responsibility toward the environment.
Challenges and Future Directions
While technology has greatly enhanced our ability to monitor climate change, challenges remain. Data privacy concerns, the digital divide, and the need for standardized data collection methods are critical issues that must be addressed. Furthermore, the reliance on technology should not overshadow the importance of traditional ecological knowledge and community-based approaches to environmental stewardship.
Looking ahead, continued investment in technology and research is crucial for effective climate monitoring. Collaboration between governments, private sectors, and academic institutions can drive innovation and facilitate the development of new tools and methodologies. As we advance, integrating technology with policy and community action will be essential in tackling the climate crisis.
In conclusion, technology plays a vital role in monitoring climate change, providing tools and insights that were once unimaginable. From satellite imagery and climate modeling to AI and citizen science, these advancements are reshaping our understanding of the planet's dynamics. As we confront the challenges posed by climate change, harnessing technology will be key to fostering resilience and promoting sustainable practices for future generations.