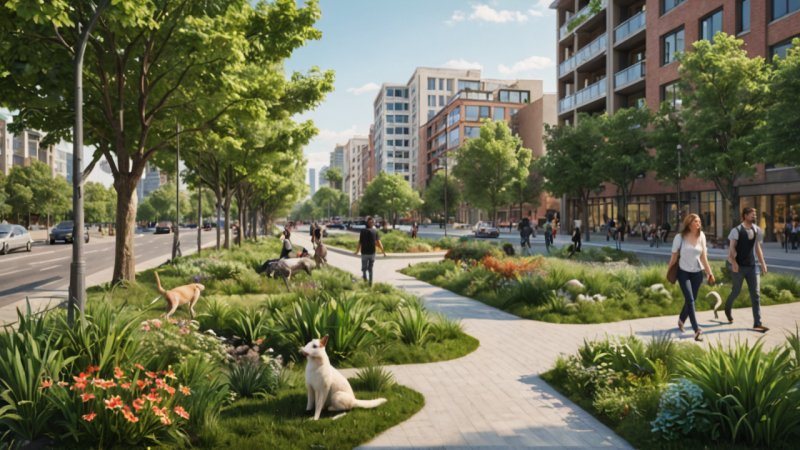
What is urbanization?
Urbanization refers to the increasing population shift from rural to urban areas, leading to the growth of cities and towns. This process often involves the conversion of natural landscapes into built environments, which can significantly impact local wildlife.
How does urbanization affect local wildlife populations?
Urbanization can lead to habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation, which often results in declines in local wildlife populations. Species that are unable to adapt to urban environments may face extinction, while others may thrive in these modified habitats.
What types of wildlife are most affected by urbanization?
Different species respond to urbanization in various ways. Birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians are all affected, but species that require large territories or specific habitats, such as large mammals and many bird species, are particularly vulnerable.
Are there any wildlife species that benefit from urbanization?
Yes, some species have adapted well to urban environments. For example, raccoons, pigeons, and certain types of insects often thrive in cities due to the availability of food and shelter. These species can sometimes outcompete their rural counterparts.
What are some strategies to mitigate the impact of urbanization on wildlife?
- Creating wildlife corridors: These are pathways that connect fragmented habitats, allowing animals to move safely between areas.
- Implementing green spaces: Parks, gardens, and green roofs can provide essential habitats for various species.
- Promoting native species: Encouraging the planting of native plants can help support local wildlife.
How does urbanization impact biodiversity?
Urbanization often leads to a decrease in biodiversity as native species are displaced by invasive species and urban-adapted organisms. This loss of biodiversity can disrupt ecosystems and reduce their resilience to environmental changes.
What role do urban planners play in protecting wildlife?
Urban planners can incorporate wildlife conservation into their designs by considering the needs of local species. This includes preserving natural habitats, creating green spaces, and ensuring that urban developments do not isolate wildlife populations.
Can urbanization lead to human-wildlife conflicts?
Yes, as wildlife adapts to urban environments, conflicts can arise. Animals may invade residential areas in search of food, leading to issues such as property damage or health risks. Effective management strategies are essential to mitigate these conflicts.
What are some successful examples of urban wildlife management?
Cities around the world have implemented successful wildlife management strategies. For instance, Singapore has integrated nature into its urban planning with extensive green spaces and wildlife corridors, promoting biodiversity while accommodating urban growth.
What can individuals do to help local wildlife in urban areas?
- Support local conservation efforts: Get involved with or donate to organizations focused on wildlife preservation.
- Create wildlife-friendly spaces: Plant native species in your garden to attract local wildlife.
- Educate others: Raise awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation in urban settings.
Are there any ongoing research studies on urbanization and wildlife?
Yes, many researchers are studying the effects of urbanization on wildlife to understand how species adapt and what conservation strategies can be effective. These studies often involve field research, data analysis, and collaboration with urban planners.
In conclusion, urbanization presents both challenges and opportunities for local wildlife. While many species face threats from habitat loss and human-wildlife conflicts, there are also strategies and initiatives that can help mitigate these impacts. By understanding the dynamics between urban environments and wildlife, we can work towards creating a more sustainable coexistence.