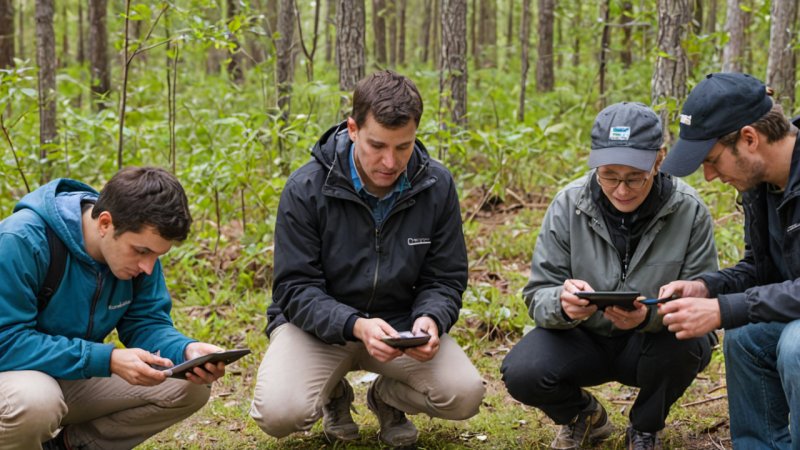
What is Citizen Science?
Citizen science refers to the involvement of the general public in scientific research, particularly in data collection and analysis. This collaborative approach allows non-professionals to contribute to scientific endeavors, often leading to significant insights and discoveries.
How Does Citizen Science Contribute to Environmental Monitoring?
Citizen science plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring by enabling communities to collect data on local ecosystems, wildlife populations, and environmental changes. This grassroots approach can provide large-scale data that is often difficult for professional scientists to gather alone.
What Are Some Examples of Citizen Science Projects in Environmental Monitoring?
- eBird: A project that allows birdwatchers to report their sightings, contributing to a global database that helps track bird populations and migration patterns.
- iNaturalist: A platform where individuals can document and share observations of plants and animals, aiding biodiversity studies.
- Globe at Night: An initiative focused on measuring light pollution by having participants record the visibility of stars in their area.
What Are the Benefits of Citizen Science?
Citizen science offers numerous benefits, including:
- Engagement: It fosters a sense of community and encourages public interest in science.
- Data Collection: It increases the volume and variety of data available for research.
- Education: Participants learn about scientific methods and environmental issues, enhancing public knowledge.
Are There Any Challenges Associated with Citizen Science?
While citizen science has many advantages, it also faces challenges such as:
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data collected by non-professionals can be difficult.
- Participant Retention: Keeping volunteers engaged over time is essential for long-term projects.
- Funding: Many citizen science projects rely on grants and donations, which can be inconsistent.
How Can Individuals Get Involved in Citizen Science?
Individuals interested in participating in citizen science can:
- Join local or online citizen science projects.
- Participate in community science events or workshops.
- Use apps and platforms designed for citizen scientists to contribute data.
What Impact Does Citizen Science Have on Policy Making?
Citizen science can influence environmental policy by providing valuable data that highlights local issues and trends. Policymakers may use this information to make informed decisions about conservation efforts, environmental regulations, and resource management.
Can Citizen Science Be Used in Other Fields Besides Environmental Monitoring?
Yes, citizen science is applicable in various fields, including:
- Public Health: Tracking disease outbreaks and health trends.
- Astronomy: Observing celestial events and contributing to astronomical databases.
- Archaeology: Engaging the public in historical research and artifact documentation.