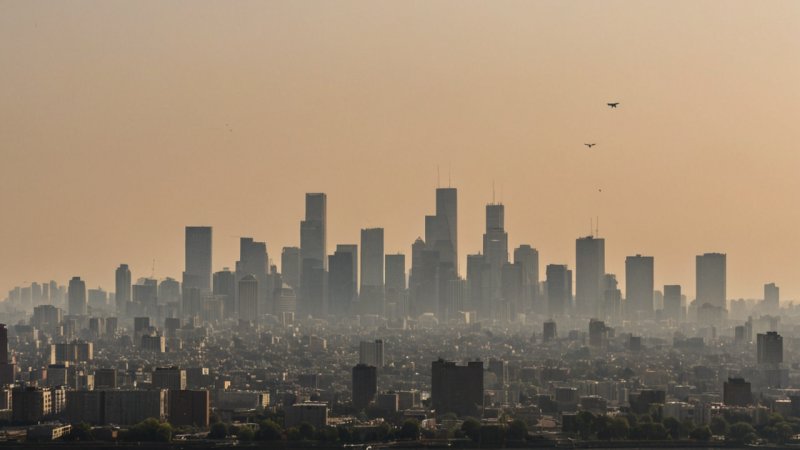
Air quality is a critical component of public health that often goes overlooked. As urbanization increases and industrial activities expand, understanding the effects of air quality on health becomes more urgent. Poor air quality is linked to a range of health issues, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even mental health disorders. This article explores the relationship between air quality and health, highlighting key research findings and trends.
Numerous studies have established a direct connection between air pollution and various health outcomes. For instance, particulate matter (PM), especially PM2.5, is known to penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution is responsible for an estimated 7 million premature deaths each year. Research indicates that long-term exposure to polluted air can lead to chronic illnesses such as asthma, bronchitis, and heart disease.
In addition to physical health, the effects of air quality extend to mental health. Recent studies suggest that exposure to high levels of air pollution may contribute to anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline. A 2020 study published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives found that individuals living in areas with poor air quality exhibited higher rates of mental health disorders compared to those in cleaner environments. This underscores the need for holistic approaches to health that consider environmental factors.
Technological advancements have played a crucial role in monitoring air quality and understanding its impacts. Innovative air quality sensors and data collection methods allow researchers to track pollution levels in real-time. This data is invaluable for identifying pollution hotspots and informing public policy. For example, cities like Los Angeles and Beijing have implemented air quality monitoring systems that help residents stay informed about pollution levels, enabling them to take precautionary measures.
Policy initiatives also play a significant role in improving air quality. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of clean air regulations. The implementation of stricter emissions standards for vehicles and industries has shown positive results in reducing pollution levels. Moreover, promoting green technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy sources, contributes to cleaner air and better health outcomes.
In conclusion, the effects of air quality on health are profound and multifaceted. As research continues to unveil the complexities of this relationship, it is essential for individuals, communities, and policymakers to prioritize clean air initiatives. By understanding the health implications of air pollution, we can advocate for policies that protect public health and foster a healthier environment for all.