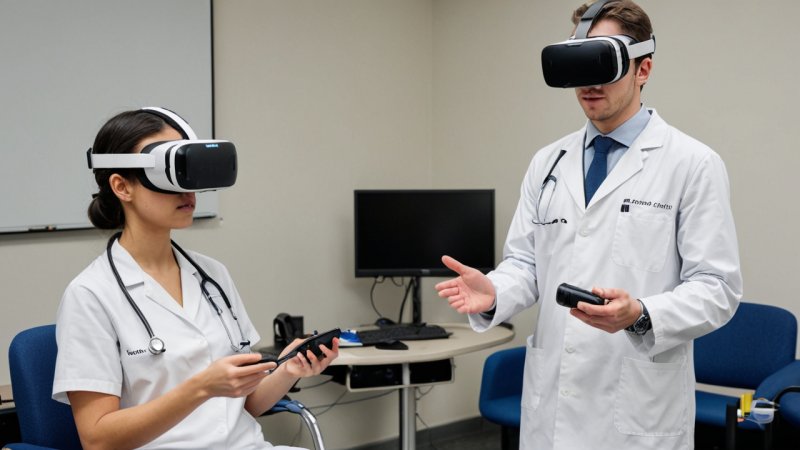
In recent years, the field of medical training has witnessed a significant transformation with the advent of new technologies. Among these innovations, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a powerful tool, offering unique advantages over traditional training methods. This article aims to compare virtual reality and conventional techniques in medical education, examining their respective benefits, drawbacks, and overall effectiveness in preparing future healthcare professionals.
Overview of Medical Training Methods
Medical training has traditionally relied on hands-on experience, lectures, and simulations. These methods include clinical rotations, cadaver dissections, and standardized patient encounters. However, as the healthcare landscape evolves, so too must the methods used to train medical professionals. Virtual reality has entered the scene as a modern alternative, providing immersive experiences that can enhance learning outcomes.
Pros of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
- Immersive Learning Experience: VR technology enables students to engage in realistic simulations, allowing them to practice procedures in a safe environment without the risk of harming patients.
- Accessibility: VR can make high-quality training accessible to students regardless of geographical location, enabling remote learning opportunities.
- Repetition and Mastery: Students can repeat procedures as many times as necessary, promoting mastery of skills before encountering real-life patients.
- Immediate Feedback: Many VR training programs provide instant feedback, helping students identify areas for improvement in real-time.
Cons of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
- High Initial Costs: The development and implementation of VR technology can be expensive, potentially limiting its adoption in some institutions.
- Technical Limitations: VR systems may face technical issues, such as software bugs or hardware malfunctions, which can disrupt training sessions.
- Limited Human Interaction: While VR can simulate clinical scenarios, it may not fully replicate the complexities of real patient interactions and communication.
Pros of Traditional Methods in Medical Training
- Real-World Experience: Traditional methods provide students with direct exposure to patients, helping them develop essential communication skills and bedside manner.
- Established Curriculum: Many traditional training programs have a long history and are well-structured, ensuring comprehensive coverage of necessary topics.
- Peer Learning: Working alongside peers and instructors in a clinical setting fosters collaboration and learning through observation and discussion.
Cons of Traditional Methods in Medical Training
- Limited Practice Opportunities: Students may have fewer chances to practice specific procedures, especially in high-stakes environments where patient safety is a concern.
- Variable Quality of Training: The quality of training can vary significantly depending on the clinical setting and available resources.
- Emotional Stress: Encountering real patients can be emotionally taxing for students, particularly when faced with difficult cases or outcomes.
Comparative Effectiveness
When comparing the effectiveness of virtual reality and traditional methods, it is essential to consider the specific skills being taught. VR excels in teaching technical skills, such as surgical procedures, where repetition and precision are critical. Traditional methods, on the other hand, are invaluable for developing interpersonal skills and understanding the nuances of patient care.
Integration of Both Approaches
Rather than viewing VR and traditional methods as mutually exclusive, many educators advocate for an integrated approach. By combining the strengths of both techniques, medical training programs can offer a more comprehensive educational experience. For example, students might learn surgical techniques through VR simulations before applying those skills in a clinical setting with real patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both virtual reality and traditional methods have their respective strengths and weaknesses in medical training. While VR offers immersive, repeatable experiences that can enhance technical skill acquisition, traditional methods provide essential real-world exposure and human interaction. The future of medical training may lie in a hybrid model that leverages the advantages of both approaches, ultimately leading to better-prepared healthcare professionals.