The intricate relationship between nutrition and mental health has garnered increasing attention from researchers and healthcare professionals alike. In recent years, a growing body of evidence suggests that what we eat can have profound effects on our mood, cognitive function, and overall mental well-being. This article delves into the various aspects of how nutrition influences mental health, highlighting key studies, nutritional components, and practical dietary recommendations that can promote better mental health outcomes.
Understanding the Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health
The connection between nutrition and mental health is multifaceted, involving biological, psychological, and social factors. Nutritional psychiatry is an emerging field that examines how dietary patterns affect mental health. Research indicates that certain nutrients play crucial roles in neurotransmitter synthesis, inflammation, and brain health, all of which are vital for maintaining mental well-being.
The Role of Nutrients
Several key nutrients have been identified as particularly important for mental health:
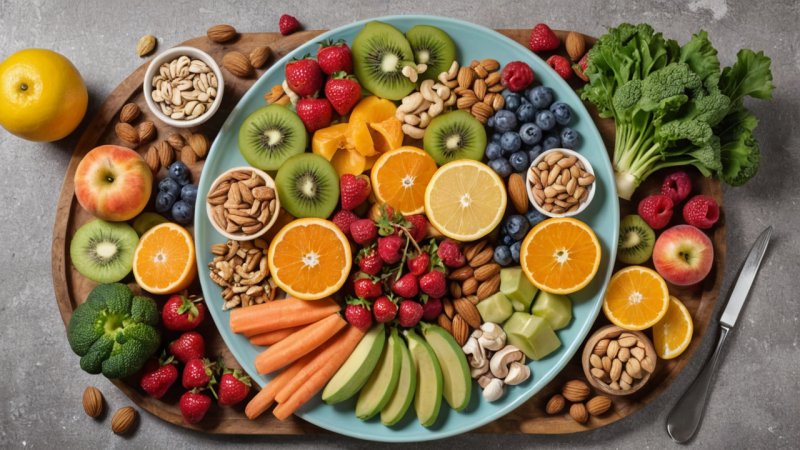
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health. Studies have shown that individuals with higher omega-3 intake have lower rates of depression and anxiety.
- B Vitamins: B vitamins, especially B12 and folate, are crucial for brain function and mood regulation. Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to increased risk of depression and cognitive decline.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help reduce oxidative stress in the brain, which is associated with various mental health disorders.
- Minerals: Minerals like magnesium, zinc, and iron play important roles in neurotransmission and mood regulation. Low levels of these minerals have been associated with increased anxiety and depression.
Key Research Findings
Numerous studies have explored the relationship between diet and mental health, providing compelling evidence for the impact of nutrition on psychological well-being.
Dietary Patterns and Mental Health
Research has indicated that certain dietary patterns can influence mental health outcomes. For example, the Mediterranean diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and healthy fats, has been associated with lower rates of depression and anxiety. A study published in the journal Psychiatric Research found that adherence to the Mediterranean diet was linked to a reduced risk of developing depressive symptoms.
Specific Nutrients and Their Impact
Several studies have focused on specific nutrients and their effects on mental health:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A meta-analysis published in Translational Psychiatry found that omega-3 supplementation significantly reduced symptoms of depression, particularly in individuals with major depressive disorder.
- B Vitamins: A study in the journal Nutrition revealed that older adults with low levels of B12 and folate were more likely to experience cognitive decline and depressive symptoms.
- Probiotics: Emerging research suggests that gut health is closely linked to mental health. A study published in Nature demonstrated that probiotics could improve mood and reduce anxiety in individuals with depressive symptoms.
Practical Dietary Recommendations
Given the evidence supporting the link between nutrition and mental health, incorporating specific dietary changes can be beneficial for mental well-being:
1. Embrace a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can provide the necessary nutrients for optimal brain function.
2. Increase Omega-3 Intake
Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids into your diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
3. Prioritize B Vitamins
Consume foods high in B vitamins, including leafy greens, legumes, eggs, and dairy products, to support mood regulation and cognitive function.
4. Focus on Gut Health
Include probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi to support gut health, which may have a positive impact on mental health.
5. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for cognitive function and mood stability. Aim to drink adequate water throughout the day.
Challenges and Considerations
While the link between nutrition and mental health is promising, several challenges remain:
1. Individual Differences
Individual differences in genetics, lifestyle, and pre-existing health conditions can influence how nutrition affects mental health.
2. Socioeconomic Factors
Access to healthy foods can be limited by socioeconomic status, which can impact dietary choices and mental health outcomes.
3. Need for More Research
While current research is encouraging, more studies are needed to fully understand the complexities of the relationship between diet and mental health.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a significant role in mental health, influencing mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being. By understanding the impact of specific nutrients and dietary patterns, individuals can make informed choices to support their mental health. As research continues to evolve, the integration of nutritional strategies into mental health care may become an essential component of holistic treatment approaches. Embracing a balanced diet, prioritizing nutrient-rich foods, and focusing on gut health can pave the way for improved mental well-being and a better quality of life.