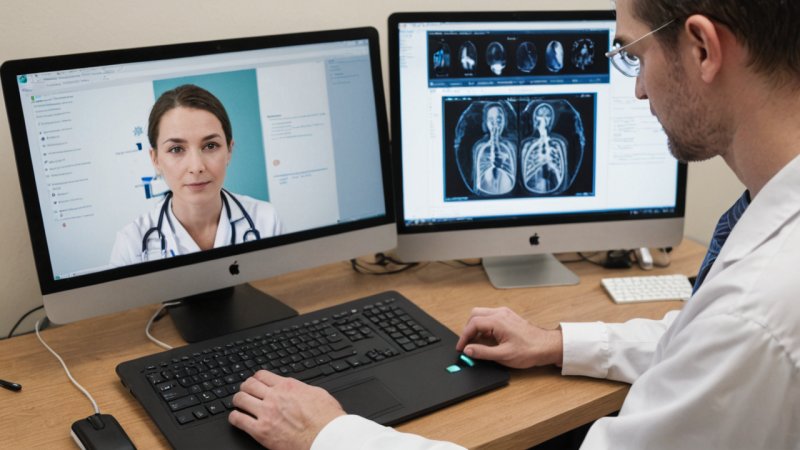
Telemedicine is not only transforming patient care but also significantly influencing medical research. As remote healthcare solutions gain popularity, researchers are exploring how telemedicine can enhance data collection, patient recruitment, and overall research outcomes. This article examines the impact of telemedicine on medical research and its potential to advance healthcare knowledge.
One of the most notable benefits of telemedicine in research is the ability to reach a broader patient population. Traditional clinical trials often require participants to travel to specific locations for assessments and visits, which can limit diversity and representation in study samples. Telemedicine allows researchers to conduct virtual assessments, enabling them to recruit participants from various geographical regions, including rural and underserved areas. This increased accessibility can lead to more comprehensive data and ultimately improve the generalizability of research findings.
Moreover, telemedicine facilitates ongoing data collection and monitoring. Many telehealth platforms incorporate tools for tracking patient symptoms, medication adherence, and other relevant metrics. This real-time data collection can enhance the quality of research by providing researchers with continuous insights into patient experiences and outcomes. With the ability to gather data remotely, researchers can conduct longitudinal studies more efficiently, capturing the long-term effects of treatments and interventions.
Another significant impact of telemedicine on medical research is the potential for improved patient engagement. By utilizing telehealth technologies, researchers can maintain regular communication with study participants. This consistent interaction can help keep participants motivated and informed about the study's progress, leading to higher retention rates and better data integrity. Engaged participants are more likely to adhere to study protocols, contributing to the reliability of research findings.
Telemedicine also opens new avenues for innovative research methodologies. For example, researchers can utilize remote monitoring devices to collect physiological data, such as heart rate or glucose levels, outside of clinical settings. This approach allows for a more holistic understanding of patient health and can lead to the exploration of new research questions that were previously challenging to address in traditional settings.
Despite its many advantages, the integration of telemedicine into medical research is not without challenges. Issues related to data privacy and security are paramount, as researchers must ensure that patient information is protected during virtual interactions. Additionally, the reliance on technology may exclude certain populations who lack access to the necessary devices or internet connectivity, potentially introducing bias into studies.
In conclusion, telemedicine is reshaping the landscape of medical research by expanding patient recruitment, enhancing data collection, and promoting participant engagement. As healthcare continues to evolve, the integration of telemedicine into research methodologies presents exciting opportunities for advancing medical knowledge. By addressing challenges and leveraging technology effectively, researchers can harness the power of telemedicine to improve health outcomes and drive innovation in the field.
Telemedicine and Its Impact on Medical Research
Telemedicine is revolutionizing not just patient care but also the landscape of medical research.