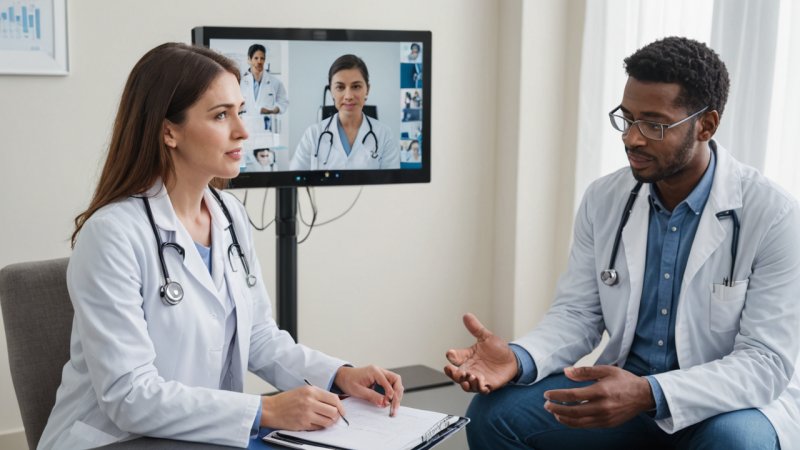
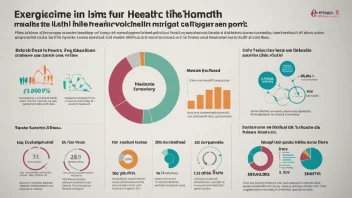
Telemedicine has emerged as a critical component of modern healthcare, transforming how patients and providers interact. With advancements in technology, telemedicine has made healthcare more accessible, convenient, and efficient, particularly for those living in remote areas or facing mobility challenges. This article explores the role of telemedicine in contemporary healthcare, its benefits, and its challenges.
Over the past decade, telemedicine has gained significant traction, with many healthcare providers integrating virtual consultations into their practices. This shift has been propelled by the need for accessible healthcare solutions, especially highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic. As traditional in-person visits faced limitations, telemedicine offered a viable alternative, allowing patients to consult healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes.
One of the most significant advantages of telemedicine is its ability to increase access to care. Patients living in rural or underserved areas often struggle to receive timely medical attention due to geographical barriers. Telemedicine bridges this gap by connecting them with specialists and primary care providers through video calls or phone consultations. This not only saves patients time and travel costs but also ensures they receive the care they need without delay.
In addition to geographic accessibility, telemedicine has proven invaluable for managing chronic conditions. Patients with diabetes, hypertension, or mental health disorders can benefit from regular virtual check-ins with their healthcare providers. These consultations allow for ongoing monitoring of their conditions, medication management, and timely interventions if needed. As a result, patients can maintain their health more effectively while enjoying the convenience of remote care.
Moreover, telemedicine has been instrumental in reducing the burden on healthcare facilities. By enabling virtual appointments, hospitals and clinics can allocate their resources more efficiently. This is especially crucial during times of crisis, such as the pandemic, where healthcare systems can become overwhelmed. Telemedicine helps to alleviate some of this pressure by allowing non-urgent cases to be managed remotely, freeing up in-person visits for those in immediate need of care.
Despite its many benefits, telemedicine also faces challenges. One of the primary concerns is the digital divide; not everyone has equal access to the internet or the necessary technology to participate in telehealth services. This can exacerbate health disparities, particularly for low-income communities or older adults who may be less tech-savvy.
Additionally, concerns about privacy and the security of patient information have emerged as telemedicine becomes more widespread. Healthcare providers must ensure they use secure platforms to protect sensitive patient data during virtual consultations.
In conclusion, telemedicine has revolutionized modern healthcare by improving access, enhancing chronic disease management, and easing the burden on healthcare facilities. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in technology and policy can help address these issues. As telemedicine continues to evolve, it holds the potential to shape the future of healthcare delivery, making it more inclusive and responsive to the needs of diverse populations.
Telemedicine: Revolutionizing Healthcare Access
Telemedicine is transforming healthcare access, making it more convenient and efficient for patients, especially those in remote areas.