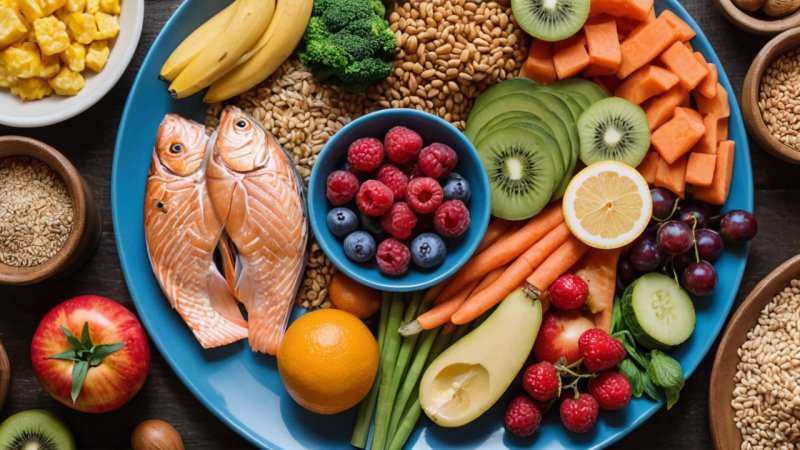
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism against pathogens, and its efficiency can be influenced by various factors, including diet. Recent scientific research has increasingly highlighted the critical role that nutrition plays in shaping immune responses. This article delves into the intricate relationship between diet and immune function, exploring how certain nutrients can enhance immunity, the consequences of dietary deficiencies, and practical dietary strategies to support a robust immune system.
Understanding the Immune System
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders. It consists of two primary components: the innate immune system, which provides immediate but non-specific defense, and the adaptive immune system, which develops a targeted response to specific pathogens. Both systems require various nutrients to function optimally.
The Role of Nutrition in Immune Function
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the immune system. Specific nutrients are essential for the development and activity of immune cells. Here are some key nutrients and their contributions:
Vitamins
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that helps protect immune cells from oxidative stress and supports the production of white blood cells.
- Vitamin D: Modulates the immune response and has been shown to enhance the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes and macrophages.
- Vitamin A: Essential for maintaining the structural and functional integrity of mucosal cells, which act as a barrier against pathogens.
Minerals
- Zinc: Critical for the development and function of immune cells, particularly T lymphocytes, and has been shown to reduce the duration of the common cold.
- Iron: Necessary for the proliferation of immune cells and the production of cytokines, which are key in immune responses.
Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help modulate immune responses and reduce excessive inflammation.
Consequences of Dietary Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can lead to immunodeficiency, making the body more susceptible to infections and diseases. For instance:
- Protein Deficiency: Insufficient protein intake can impair the production of antibodies and other immune cells.
- Micronutrient Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc, can lead to weakened immune responses and increased vulnerability to infections.
Dietary Strategies to Enhance Immune Function
To support and enhance immune function, it is essential to adopt a balanced and varied diet. Here are some practical dietary strategies:
Incorporating a Variety of Foods
A diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the spectrum of nutrients necessary for optimal immune function. Aim for a colorful plate, as different colors often indicate different nutrient profiles.
Prioritizing Whole Foods
Whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, are nutrient-dense and provide essential vitamins and minerals that support immune health. Minimize processed foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, as they can negatively impact immune function.
Staying Hydrated
Water is crucial for overall health and helps maintain the balance of bodily fluids, which is essential for immune function. Aim for adequate hydration by drinking water and consuming hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables.
Probiotics and Gut Health
The gut microbiome plays a significant role in immune function. Consuming probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, can enhance gut health and, in turn, support immune responses.
Research Insights and Case Studies
Numerous studies have explored the link between diet and immune function. For example, a study published in the journal Nature Reviews Immunology highlighted how a diet rich in antioxidants can enhance the functionality of immune cells. Another research article in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry demonstrated that specific dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, are associated with reduced inflammation and improved immune responses.
Case Study: The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and healthy fats, has been linked to numerous health benefits, including enhanced immune function. Research indicates that this diet can reduce the risk of chronic diseases and improve the body’s ability to fight infections.
Conclusion
In summary, diet plays a crucial role in supporting and enhancing immune system function. A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can bolster immune responses and reduce the risk of infections. Conversely, dietary deficiencies can lead to weakened immunity and increased susceptibility to diseases. By prioritizing whole foods, incorporating a variety of nutrients, and adopting healthy dietary practices, individuals can promote their immune health and overall well-being. As research continues to uncover the intricate connections between diet and immune function, it is clear that what we eat significantly influences our body’s ability to defend itself against pathogens.