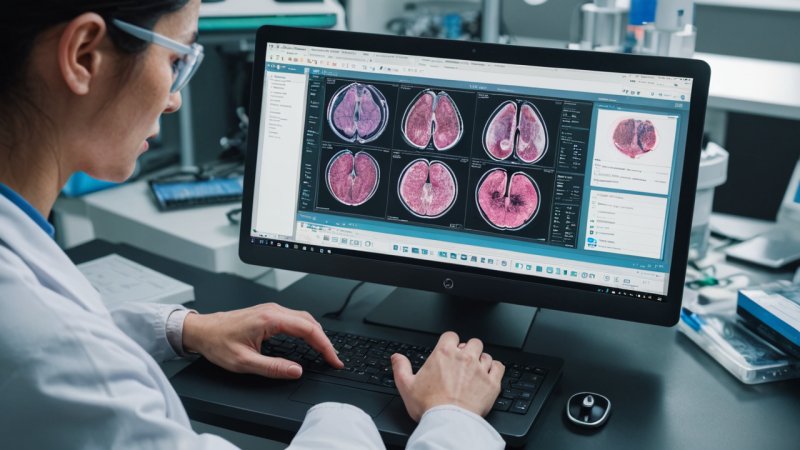
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly changing the landscape of various fields, and pathology is no exception. As a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis of disease through the examination of organs, tissues, and bodily fluids, pathology has always relied heavily on the expertise of trained professionals. However, with the advent of AI technologies, the potential for enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and innovation in this field has never been greater. This article delves into the ways AI is improving pathology, explores key advancements, discusses challenges, and examines the future of this integration.
Understanding Pathology and the Role of AI
Pathology is often referred to as the "science of disease" and plays a critical role in the medical field. Pathologists analyze samples from patients to diagnose diseases, including cancers, infections, and autoimmune disorders. Traditionally, this process involves meticulous examination of slides prepared from tissue biopsies, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
AI, particularly through machine learning and deep learning algorithms, offers the potential to automate and enhance these diagnostic processes. By training algorithms on vast datasets of annotated pathology images, AI can learn to recognize patterns indicative of various diseases, providing pathologists with powerful tools to assist in diagnosis.
Key Advancements in AI-Driven Pathology
The integration of AI into pathology has led to several significant advancements:
- Image Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze pathology slides with remarkable speed and accuracy. For instance, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have shown efficacy in identifying cancerous cells within tissue samples, often achieving accuracy rates comparable to human pathologists.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze patient data alongside pathology results to predict outcomes and recommend personalized treatment plans. This capability is particularly valuable in oncology, where treatment decisions can be complex.
- Workflow Optimization: AI tools can streamline laboratory workflows by automating repetitive tasks, such as slide scanning and preliminary analysis, allowing pathologists to focus on more complex diagnostic challenges.
- Telepathology: AI enhances telepathology, enabling remote diagnosis and consultation. This is especially beneficial in underserved areas where access to specialist pathologists may be limited.
Case Studies: AI in Action
Several studies and implementations illustrate the successful application of AI in pathology:
1. Stanford University Study on Skin Cancer Detection
A team at Stanford University developed a deep learning algorithm capable of diagnosing skin cancer from images of skin lesions. The model was trained on over 130,000 images and demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy that surpassed that of experienced dermatologists.
2. PathAI's Diagnostic Support
PathAI is a company that uses AI to assist pathologists in diagnosing diseases more accurately. Their software analyzes pathology slides and provides feedback on potential diagnoses. In clinical trials, PathAI's technology has shown to improve diagnostic accuracy for various cancers.
3. Google Health's Breast Cancer Study
Google Health developed an AI model that analyzes mammograms for breast cancer detection. In a study published in 2020, the model outperformed human radiologists in identifying cancerous lesions, demonstrating the potential for AI to enhance diagnostic capabilities.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising advancements, the integration of AI into pathology is not without challenges:
- Data Quality: The effectiveness of AI algorithms depends on the quality and diversity of the training data. Ensuring that datasets are representative of various demographics and conditions is crucial for minimizing bias.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The medical field is highly regulated, and AI technologies must undergo rigorous validation before they can be widely adopted. Navigating these regulatory pathways can be complex and time-consuming.
- Acceptance by Professionals: Pathologists and medical professionals may be hesitant to adopt AI technologies due to concerns about reliability and the fear of being replaced. Education and transparency about AI's role as a supportive tool are essential.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in healthcare raises ethical questions regarding patient data privacy, consent, and the implications of algorithmic decision-making.
The Future of AI in Pathology
The future of AI in pathology is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at overcoming current challenges. As AI technologies continue to evolve, we can expect:
- Increased Accuracy: As algorithms become more sophisticated, the accuracy of AI-driven diagnostics will improve, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Integration into Clinical Practice: AI tools will likely become standard components of pathology workflows, seamlessly integrating into existing systems to enhance efficiency.
- Collaborative Diagnosis: The future may see a collaborative approach where AI and human pathologists work together, combining the strengths of both to achieve optimal diagnostic accuracy.
- Expansion Beyond Pathology: The lessons learned from AI in pathology may influence other areas of medicine, leading to broader applications in diagnostics and patient care.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize the field of pathology, offering tools that enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline workflows, and ultimately improve patient care. While challenges remain, the ongoing advancements in AI technology and its integration into clinical practice hold great promise for the future of medicine. As we continue to explore the potential of AI, it is essential to approach this transformation with a focus on ethical considerations, data quality, and the collaboration between technology and human expertise. The journey of AI in pathology is just beginning, and its impact will be felt for years to come.