The integration of technology in civil engineering project management has revolutionized how projects are planned, executed, and monitored. As the industry grapples with increasing complexity and the demand for efficiency, technology emerges as a pivotal force driving innovation. This article explores five significant ways that technology is reshaping civil engineering project management, making it more efficient, collaborative, and responsive to challenges.
1. Enhanced Project Planning with BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is at the forefront of technological advancements in civil engineering. This 3D modeling tool allows engineers and architects to visualize projects before construction begins, leading to improved planning and coordination. Key benefits of BIM include:
- Visualization: Stakeholders can see a realistic representation of the project, helping to identify potential issues early.
- Collaboration: BIM enables real-time collaboration among various teams, reducing misunderstandings and errors.
- Cost Efficiency: By identifying problems in the planning phase, BIM can help avoid costly changes during construction.
2. Real-Time Data Analytics
The ability to analyze data in real-time is transforming decision-making in civil engineering. Project managers can now leverage data analytics tools to monitor project progress, resource allocation, and budget adherence. Some of the advantages include:
- Informed Decisions: Access to real-time data allows for quick adjustments to project plans, enhancing responsiveness to emerging challenges.
- Predictive Analysis: Historical data can be analyzed to predict future trends, helping managers to anticipate issues before they arise.
- Performance Tracking: Continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) ensures that projects stay on track.
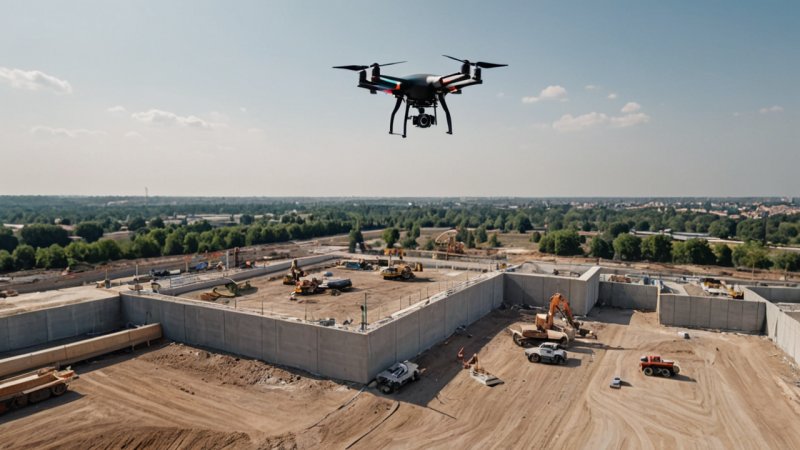
3. Drones and Aerial Surveying
Drones have become invaluable tools in civil engineering, particularly for surveying and monitoring construction sites. Their applications include:
- Site Surveys: Drones can quickly and accurately map large areas, providing essential data for project planning.
- Progress Monitoring: Aerial imagery allows project managers to assess progress and compliance with plans without needing to be on-site.
- Safety Inspections: Drones can inspect hard-to-reach areas, reducing risks for workers and improving safety compliance.
4. Cloud-Based Collaboration Tools
Cloud technology has transformed how teams collaborate on civil engineering projects. With cloud-based tools, project information is accessible to all stakeholders, regardless of location. Benefits include:
- Accessibility: Team members can access project documents and data from anywhere, facilitating remote work and collaboration.
- Version Control: Cloud platforms ensure that everyone is working from the most current project documents, reducing confusion and errors.
- Streamlined Communication: Integrated communication tools allow for seamless discussions and updates among team members.
5. Sustainable Practices through Technology
Technology is also driving sustainability in civil engineering project management. Innovations in materials and processes help reduce environmental impact. Key aspects include:
- Green Materials: Advanced materials technology allows for the use of sustainable resources that minimize environmental footprints.
- Energy Efficiency: Smart technologies can optimize energy use in construction processes, contributing to greener projects.
- Waste Reduction: Technology helps in planning and executing projects that minimize waste, promoting a circular economy.
In conclusion, the impact of technology on civil engineering project management is profound and multifaceted. From enhanced planning through BIM to the use of drones for site surveying, technology is streamlining processes, improving collaboration, and fostering sustainability. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing these technological advancements will be crucial for meeting the demands of modern civil engineering projects.