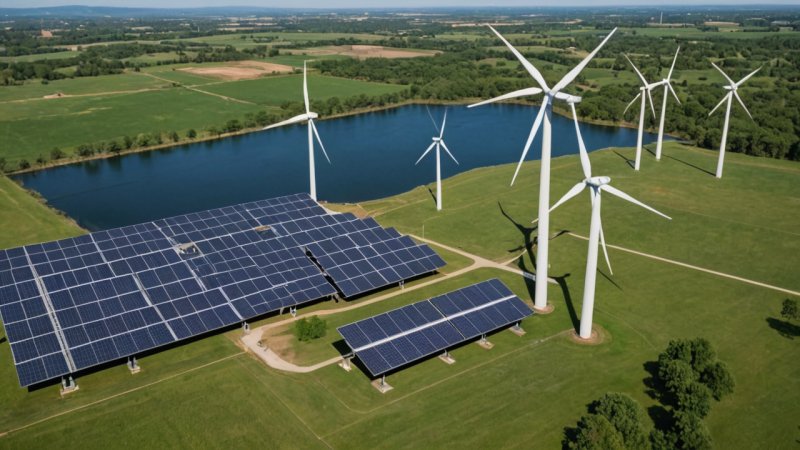
The global shift towards renewable energy sources has become imperative in the face of climate change, resource depletion, and the need for sustainable development. Engineering plays a pivotal role in shaping renewable energy policies, driving innovation, and ensuring the practical implementation of these policies. This article delves into the multifaceted relationship between engineering and renewable energy policy, exploring how engineering principles inform policy decisions, the challenges faced in the integration of renewable technologies, and the future outlook for engineering in this vital sector.
Understanding Renewable Energy
Renewable energy refers to energy derived from natural processes that are continuously replenished. This includes sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass. Each of these energy sources presents unique engineering challenges and opportunities that must be addressed to develop effective policies.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
- Solar Energy: Harnessing sunlight through photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems.
- Wind Energy: Utilizing wind turbines to convert kinetic energy into electricity.
- Hydroelectric Energy: Generating power through the flow of water, typically in dams.
- Geothermal Energy: Tapping into the Earth's internal heat for electricity generation and direct heating.
- Biomass Energy: Using organic materials as fuel for energy production.
The Role of Engineering in Renewable Energy Policy
Engineering is integral to the development and implementation of renewable energy policies. Engineers are tasked with designing systems that are not only efficient but also compliant with regulatory frameworks. Their expertise is crucial in translating theoretical policies into practical applications.
Policy Development and Engineering Insights
Effective renewable energy policies must be grounded in engineering principles. Engineers contribute to policy development by providing data-driven insights into the feasibility and efficiency of various technologies. For instance, the design of solar panels and wind turbines must consider local climate conditions, resource availability, and technological advancements. Policymakers rely on engineering analyses to understand the potential impact of renewable energy projects on the grid and the environment.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
Engineering drives innovation in renewable energy technologies. Continuous research and development lead to improved efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced performance of renewable systems. For example, advancements in battery storage technology are crucial for addressing the intermittent nature of solar and wind energy. Engineers work on developing smart grid technologies that can better integrate these renewable sources into existing power systems.
Challenges in Engineering and Policy Integration
Despite the significant progress in renewable energy technologies, several challenges hinder the effective integration of engineering solutions into policy frameworks.
Regulatory Barriers
Many regions face outdated regulatory frameworks that do not accommodate new technologies. Engineers must navigate these barriers to implement innovative solutions. For instance, permitting processes for wind farms can be lengthy and cumbersome, delaying project timelines and increasing costs.
Funding and Investment
Engineering projects often require substantial upfront investment. Policymakers must create financial incentives and funding mechanisms to encourage investment in renewable technologies. Engineers can assist by providing cost-benefit analyses that demonstrate the long-term savings associated with renewable energy adoption.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public acceptance of renewable energy projects is crucial for their success. Engineers play a role in educating the public about the benefits and safety of renewable technologies. Community engagement initiatives led by engineers can help build trust and support for renewable energy projects.
Future Outlook for Engineering in Renewable Energy Policy
The future of renewable energy policy will increasingly rely on engineering innovation. As technology evolves, so too will the policies that govern energy production and consumption. Engineers will be at the forefront of this evolution, developing solutions that address emerging challenges such as climate change, energy security, and economic sustainability.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells, advanced nuclear reactors, and carbon capture and storage, are on the horizon. Engineers will be essential in researching and developing these technologies, ensuring they are safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
Global Collaboration
The transition to renewable energy is a global challenge that requires collaboration across borders. Engineers will need to work with international organizations, governments, and private sectors to share knowledge and best practices. This collaboration can lead to the establishment of global standards and policies that promote renewable energy adoption.
Conclusion
The significance of engineering in renewable energy policy cannot be overstated. Engineers are crucial in developing innovative solutions, informing policy decisions, and overcoming challenges in the transition to renewable energy. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the collaboration between engineering and policy will pave the way for a clean energy revolution. By understanding the interplay between engineering and renewable energy policy, we can better appreciate the role of technology in shaping a sustainable world.