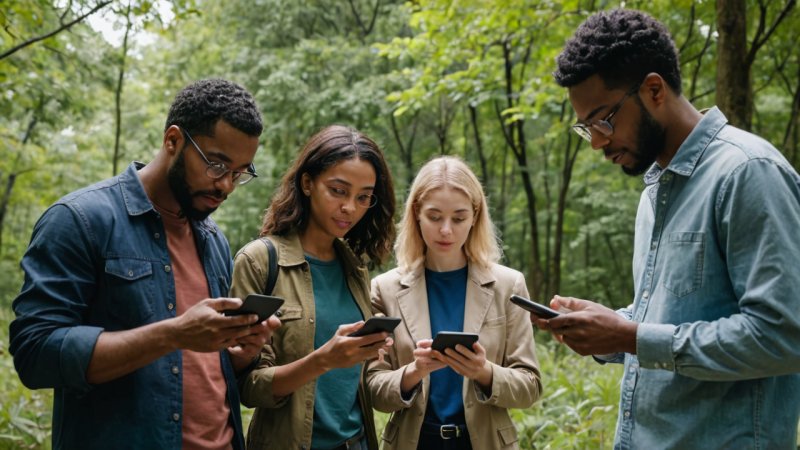
In recent years, the concept of citizen science has gained significant traction, transforming the landscape of academic research. By engaging volunteers in scientific studies, researchers are able to harness the power of the public to collect data, analyze results, and even contribute to groundbreaking discoveries. This collaborative approach not only enhances the scope of research but also democratizes science, making it more accessible to everyone.
The rise of citizen science can be attributed to advancements in technology. With the proliferation of smartphones and the internet, individuals can easily participate in research projects from anywhere in the world. For instance, apps that allow users to report wildlife sightings or track environmental changes have empowered communities to contribute valuable data. This participatory model has led to significant findings, such as tracking migratory patterns of birds or monitoring air quality in urban areas.
Moreover, citizen science fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among participants. When individuals contribute to scientific research, they develop a deeper understanding of the scientific process and the issues at hand. This engagement can lead to increased awareness and advocacy for various causes, from climate change to public health. For example, projects like Zooniverse allow volunteers to classify galaxies and identify animal species, making them active participants in the research process.
However, the integration of citizen science into traditional research methodologies is not without challenges. Ensuring data quality is a primary concern, as volunteer-collected data may vary in reliability. Researchers must implement training programs and validation processes to maintain rigorous standards. Additionally, there may be ethical considerations regarding the involvement of non-professionals in research, particularly in sensitive areas like medical studies.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of citizen science are profound. It not only expands the reach of research but also accelerates the pace of scientific discovery. Projects that would typically take years to complete can be accomplished in a fraction of the time with the help of enthusiastic volunteers. Furthermore, citizen science can lead to unexpected findings, as diverse perspectives often yield innovative insights.
In conclusion, citizen science represents a transformative shift in how research is conducted. By leveraging the collective efforts of the public, scientists can tackle complex problems more effectively and inclusively. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for citizen science to contribute to significant scientific advancements will only grow, heralding a new era of collaboration between researchers and the communities they serve.